What Is Cloud Computing And What Are The Benefits, Risks Involved

Cloud computing is a “hype topic” on everyone’s lips. The growth figures have been in the double digits for years – in business, cloud computing is therefore seen as a mega trend in the high-tech industry.
Using memory, software, or even entire infrastructures without investing in expensive hardware or licenses is also interesting for private users.
And that’s not just limited to uploading your pictures to photo databases like Picasa or Dropbox and sharing them with friends.
But what about the successful model of cloud computing? Is it safe to use, and what do you have to watch out for? This article is intended to provide a brief introduction and assistance.
What is cloud computing?
But, cloud computing means that part of the hardware or software is no longer operated by the user but is rented as a service from one or more providers.
The applications and data are no longer on the local computer, but on different servers, usually without being able to say precisely where they are at the moment. You are in the “cloud.” Access is via the Internet.
The range of offers ranges from sending messages via web-based mail service, from web storage options for photos to highly complex, scalable applications for companies and organizations. Most users have been using cloud computing in its original form for many years.
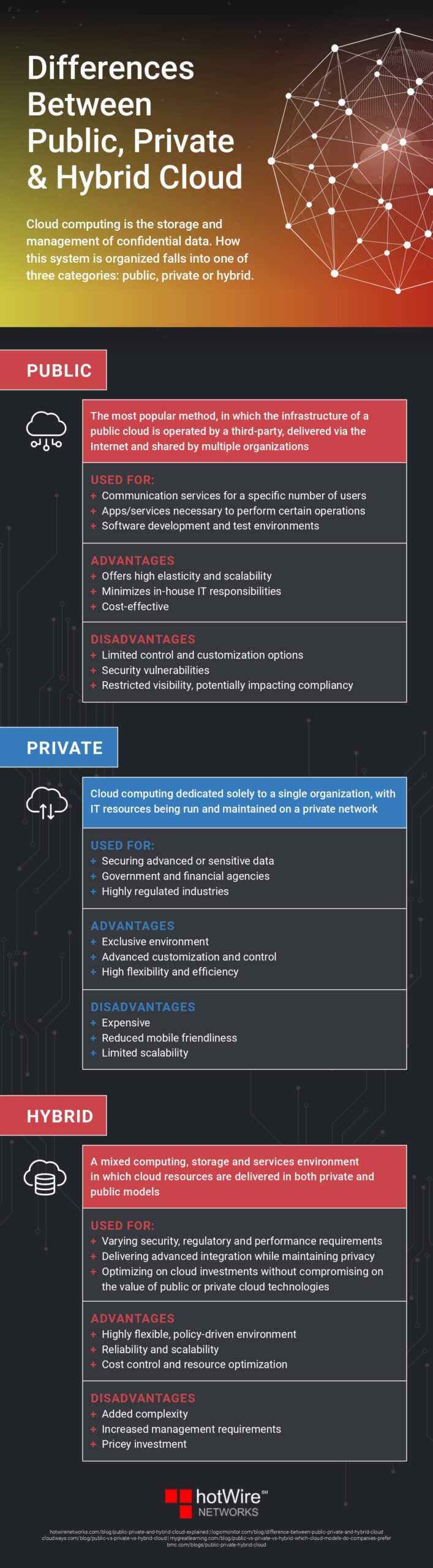
Types of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be divided into two forms and three service types:
- The public cloud – the “public cloud” – provides access to IT services for the general public via the Internet. For example, users can rent infrastructure flexibly and adapt it to their individual needs.
- The private cloud – the private computer cloud – includes access to a protected, delimited area, for example, within one’s organization.
- The mixed form of public cloud and private cloud is called hybrid cloud (“hybrid” = Latin “mixed”) and represents a combination of public and private areas according to the needs of their users.
Cloud computing includes various service models, some of which are difficult to distinguish. Essentially, however, three types can be distinguished:
- IaaS (“Infrastructure as a Service” = “Platform as a Service” ): With this model, the user can access outsourced hardware infrastructure when needed (“on demand”), for example, if there is an increased need for computing power. A good example is online shops requiring larger computer capacity at Christmas time. Instead of buying more powerful and, therefore, more expensive servers that are not needed to the same extent for the rest of the year, the shops can rent additional external capacities from a provider such as Amazon (“Amazon EC2”).
- PaaS (“Platform as a Service” = platform as a service): This model is primarily intended for developers and usually offers services and applications in addition to the interface.
- SaaS aaS (“Software as a Service” = software as a service): It is the “smallest” form of cloud computing and is, therefore, probably the most important for private users. Here only individual applications are usually used via the web browser. All the user needs for this is an Internet-enabled PC. The provider provides them with the software they want to use. The largest provider of SaaS solutions is Salesforce.com; well-known applications include Google Drive or the cloud version of the Microsoft Office package, Office 365.
Benefits of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing also offers undeniable advantages for private users:
- Availability: If the user has placed his data, for example, his photos or documents, in the cloud, he can access them from anywhere and with any internet-enabled device.
- Cost Savings: The user can always access the latest programs without purchasing them. Therefore, there are no acquisition costs, which can quickly amount to a few hundred euros, especially with high-quality and complex programs. Adobe Acrobat is an example. With the cloud solution, the software for creating PDF files only costs the user a few monthly euros. Larger storage capacities can also be obtained at a low cost.
- Up-to-date programs: The applications are always up-to-date without the user having to worry about it. Of course, the new purchase for program updates is also not necessary.
- Security: The user does not have to worry about anything. The provider ensures that updates are installed, and regular backups are created, for example. Even non-technical users can be sure of using applications or the like.
Risks in Cloud Computing
However, the user must be aware that there are also risks when using cloud computing services in addition to the advantages. The security of the data is
- about the protection of your data and
- concerning the availability and integrity, i.e., the intactness of your data,
The biggest vulnerability.
Commercial companies face challenges when using the cloud. On the other hand, it is usually not particularly relevant for private users.
For example, only interoperability and portability hurdles are mentioned here, i.e., problems arising if you want to transfer your data from one provider to another.
Protection of your data
The user naturally is interested in the provider of cloud computing services not passing on his data to third parties without authorization, for example, for commercial purposes.
It is, therefore, imperative to pay attention to the general terms and conditions of the provider. Permission is often found here for specific data to be passed on.
This is especially the case with free offers since the data sale is the provider’s only income source. You should consider whether you should not instead choose a paid offer where you can be sure that your data will remain untouched.
Data availability and integrity
Other essential points for private users are the availability and integrity of the data. Providers often advertise by pointing out the risk of data loss if your hard drive crashes.
Storing the data in the cloud is, therefore, more secure. Nothing is more annoying when the data cannot be provided at the desired time or – even worse – that it has been destroyed due to technical difficulties.
You should, therefore, always ensure in advance that you are dealing with a reputable provider with the technical know-how and the capacities to protect the data entrusted to him in the best possible way.
You should also ensure that the provider does not exclude liability for data loss. Therefore, if in doubt, it is better to spend a few euros more.
Third-Party Data
As a rule, private users do not fall under the provisions of the Federal Data Protection Act, as long as the data is only stored for family and personal activities ( 1 Para. 2 No. 3 BDSG).
In individual cases, however, it isn’t easy to differentiate. For example, the exchange of information within an association can no longer be classified as personal and private.
The scope of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) may also apply if personal data is processed fully or partially automatically or if non-automated processing is to be stored in a file system (Art. 2 Para. 1 GDPR, Art. 4 GDPR).
In addition, if the data placed in the cloud falls into the hands of third parties and is misused, the user may be held liable for violating general personal rights.
Therefore, you should always exercise caution and consider which data you entrust to the cloud. When in doubt, less is more here.
Infographic created by HotWire Networks
Conclusion
Cloud computing also offers a wealth of advantages for private users. But you have to be aware of the risks involved.
- Does the cloud computing provider look reputable? If in doubt, use a search engine to research whether there are negative reviews or other relevant information.
- Check the contract/terms and conditions. Especially with free offers, the provider is often given extensive access options to the data stocks. Rather spend a few euros with another provider and then be on the safe side. The question of liability in the event of data loss is also essential.
- Take a look at the provider’s security concept. Does he take adequate precautions against data loss or data theft? Certification is best here, for example, according to the Federal Office for Information Security (BSI) criteria.
- Caution must be exercised when uploading personal data from third parties to the cloud. Even as a private user, you can also be subject to the Federal Data Protection Act or the General Data Protection Regulation or be liable for unauthorized use of the data by third parties due to a violation of general personal rights.